The Powder Keg of the Levant--How Sectarian Power Structures Guarantee Perpetual Instability
In the ancient lands of the Levant, where history is measured in millennia, a modern curse condemns nations to a purgatory of weakness. This is not a curse of geography or resources, but one of design—a political architecture built not on the bedrock of principled compromise and shared national vision, but on the shifting sands of sectarian appeasement. The fates of Lebanon and Syria stand as stark, bloody testaments to a brutal truth: a government forged in the fire of sectarian civil war is destined to be weak, illegitimate, and a prelude to the next conflict.
One would think that healing and reconciliation should follow three decades of peace. Yet Lebanon, whose 15-year civil war ended 35 years ago, is a nation frozen in time, a ghost haunting its own corpse. It is not a healed nation but a palimpsest of its former conflicts, its power structures meticulously drawn along the very sectarian lines that once tore it apart.
This is a country still ruled, in effect, by unelected leaders. The current president was appointed after years of vacuum, his ascent only possible by twisting the constitution to bypass a rule prohibiting active military officers from political office. The prime minister, a respected former international judge, was less elected than selected, installed through backroom compromise and heavy-handed pressure from foreign capitals like Washington, Paris, and Riyadh. Even the speakership, held by an elected MP, is shackled to a sectarian quota, its legitimacy perpetually questioned.
This patched-together entity now dares to act as a legitimate government, attempting to change the very practices its own flawed existence perpetuates. But a house divided against itself cannot stand, and a government built on sectarian compromise cannot govern. It will either fracture under the weight of its own contradictions or push ahead with its agenda, inevitably alienating one faction or another and risking a return to the civil war days it was designed to prevent. In Lebanon, the peace is the war, continued by other means.
This tragic model is not unique. Libya, shattered since 2011, is a mosaic of rival fiefdoms. A weak, internationally recognized government controls the capital, while the rest of the country answers to another regime in Benghazi or to autonomous tribal forces. There is no central authority, only a precarious and violent stalemate.
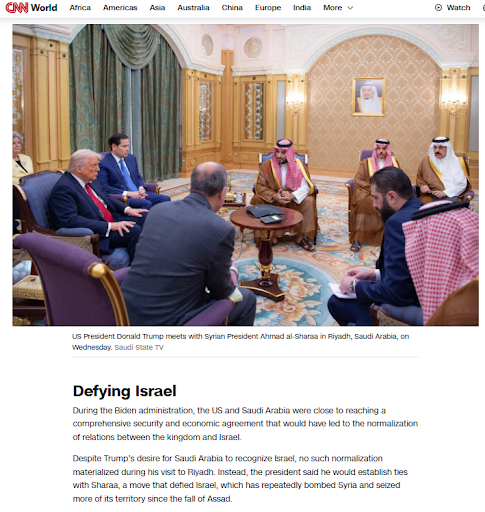
But it is Syria that presents the most chilling and recent case study. After a decade of brutal war exacerbated by a proxy conflict involving regional and global powers, the Baathist regime finally collapsed nearly a year ago. The rebels, aided by Turkey and Qatar and spearheaded by factions with extremist ideologies, seized their moment amidst the regional instability sparked by the war in Gaza.
Their victory, however, was merely the prelude to the next chapter of failure. The new Damascus regime, finding its authority challenged, has already resorted to the same tactics of its predecessor: massacres in Alawite and Druze regions, sowing fear among all ethnic and religious minorities. This has not consolidated power; it has shattered it further. The powerful Kurds, along with other groups, are now arming themselves for survival, refusing to hand their weapons to a central government they see as just another sectarian predator.
The outcome is inevitable. Syria is rapidly descending into the Lebanese and Libyan model—a central government that lacks both the legitimacy to command respect and the power to enforce its will. It rules not by consent but by fear, and fear is a fuel that quickly burns out, leaving only the ash of resentment.
When you add Iran to the mix, a country that was destabilized by US invasion and governed through a power-sharing arrangement still, the entire Levant thus becomes a powder keg, its nations condemned to cycles of violence by a refusal to transcend sectarian and tribal identities. The power of the gun, mistaken for political power, creates only a brutal illusion of control. True legitimacy is not seized through the barrel of a rifle or assigned by religious quota; it is earned through the principled compromise of a social contract that serves all citizens equally.
Without this fundamental transformation—without building states for all citizens rather than fiefdoms for sects—the next ten years will not bring peace. They will bring more transformative, and likely armed, events. The civilians of this ancient region will be lucky to witness change that is not delivered by a bullet. For now, their destiny remains held hostage by the very structures claiming to save them, guaranteeing that instability is not a phase, but a permanent condition.